Hearts and Arrows diamonds are precision-cut variations of the traditional 57 faceted round brilliant cut. They are cut to ideal proportions with good optical symmetry, polish and a specific faceting pattern.
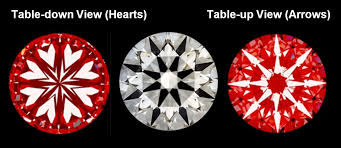
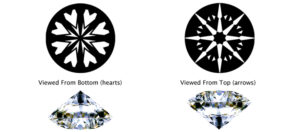
‘Hearts and arrows’ refers to the pattern that can be viewed on a virtually perfect Round Brilliant diamond. It is quite remarkable. If you look at this diamond cut using a special viewer from the top, eight arrowheads are visible. If you look at the pattern from the bottom, hearts can be seen.
When all these factors are present, the result is a repeatable, near perfect pattern of eight symmetrical arrows in the face-up position of the stone (called ‘crown’) and eight symmetrical hearts when viewed in the table-down position (called ‘pavilion’).
This was discovered in Japan in 1980 when assessing a diamond of perfect symmetry. These diamonds became highly sought after and in the 1990s they also became popular in the US.
These diamonds are exceptionally rare. In fact, it is believed that less than one per cent of Round Brilliant diamonds boast such incredible symmetry. Since this discovery, a special hearts and arrows viewer has been released onto the market to help decipher a diamond’s optical symmetry.

Design factors
The original Hearts and Arrows were diamonds that surfaced in the mid 1980s in Japan that embodied three important design factors. The first of these factors was that they were cut to what is known in the diamond industry as “ideal proportions,” i.e. very close to those summarized by Marcel Tolkowsky in his 1919 book, Diamond Design.
Second, they were cut with very good physical and optical symmetry so that they would garner the grade of “Excellent” in the system used by Japanese laboratories.
The third important factor was that they were cut to a very specific brilliantine scheme to produce the accepted hearts and arrows pattern. This faceting scheme involves prescribed lengths and ratios as well as smaller table sizes that are imperative in producing a distinctive, repeatable and gradable hearts and arrows pattern.
Less than 1% of the world’s diamonds are cut to hearts and arrows optical symmetry precision. This is in large part due to the greater amount of rough diamond that necessitates additional polishing to create diamonds with this precise optical symmetry. Diamond polishers take up to three times longer to cut diamonds of this quality and nearly 15% greater waste of the original diamond rough material is lost. Using 100X magnification and analysis through all stages of production, the artisan cutters create perfection at 10X global standards for grading and evaluation. Diamonds cut in this way are more expensive than average cut diamonds.
Hearts and Arrows viewer
To see the hearts and arrows pattern in a diamond, a specially designed light-directing viewer called a Firescope is used. The hearts and arrows viewer is a simple device that allows the viewer to analyze the physical symmetry, contrast and alignment of facets of a diamond by viewing the stone through both the top (crown area) and bottom (pavilion area) of a diamond, by directing white and coloured light at set angles in order to catch and reflect light back from specific facets and angles of the diamond.
Hearts and Arrows certification and scientific and technical research
In the early mid-1990s when Hearts and Arrows (aka H&A) began to appear in America, they were of a much higher standard than the grading laboratories were used to dealing with.
When the GIA began to encounter H&A diamonds several key characteristics were noted in the report. The diamonds were extremely round, tables were 55-57%, the girdles were medium, or thin to medium, and polish and symmetry were excellent. This kind of consistent cutting was unheard of at the time and cut grading did not yet exist in America.
HRD (Hoge Raad voor de Diamant) applies objective criteria and uses an automatic measuring device developed in-house to determine whether a diamond meets the stringent Hearts & Arrows standard.
IGI (International Gemological Institute) is also one of the laboratories that certify Hearts and Arrows.
The WTOCD (Wetenschappelijk technish Onderzoeks Centrum voor Diamand) is one of the most important scientific and technical research centres for diamonds. A proprietary software was developed by WTOCD to analyse the images according to the H&A by HRD Antwerp guidelines. Based on measurements of the H&A patterns, an expert system makes an evaluation of the guidelines. The system delivers consistent, objectively measured, H&A grades.
Diamonds with a Hearts and Arrows cut command a price premium in the world’s market, reflecting the generally greater time needed to produce them and the greater loss of
weight from rough, as well as their generally better overall cut quality. It has also become a popular sales tool in diamond marketing. Although the “Hearts and Arrows” property is indicative of a top-tier cut, it does not always mean the diamond will be the most brilliant, and should be looked at in conjunction with the cut grade. However, a Hearts and Arrows grading in conjunction with Excellent or Ideal cut grade will give a superb sparkle.

Hearts and Arrows labelling
Some in the diamond industry disagree on which diamonds should receive the “Hearts and Arrows” label. Because there used to be no industry standard, one person or company may say a diamond is a Hearts and Arrows diamond, while another may say it is not. In the industry the term “Super Ideal” is a common term that is coined and used to describe diamonds displaying perfect optical symmetry. Most diamonds with an overall cut graded by GIA as “Excellent” (with Excellent symmetry as well) or American Gem Society as “0” (or “Ideal”) will have some sort of hearts and arrows pattern when seen through a viewer, although the pattern may not be perfect. Many within the diamond industry believe the Hearts and Arrows pattern should be graded, and only those with the top grade should be called Hearts and Arrows. Those people believe that the mere presence of a Hearts and Arrows pattern is not sufficient to be considered a Hearts and Arrows diamond; the pattern must be perfect to fit within certain guidelines.
There are generally five main components that help to define a ‘Hearts and Arrows” super-ideal cut diamond. These include a diamond’s:
- Pavilion angle range: 40.2° – 41.2° (40.6° – 40.8° is optimum)
- Crown angle range: 33.4° – 36.4° (34° – 35° is optimum)
- Table size range: 53% To 58% (54%-57% is optimum)
- Lower girdle halves length range: 75% To 80% (77% is optimum)
- Star facets length range: 40% To 58% (45%-50% is optimum) [2]
Nowadays IGI and HRD grade Hearts & Arrows optimal cut, and IGI have a specific certificate. GIA does not grade Hearts & Arrows cuts, although GIA certificates will sometimes contain a note stating H&A “Laser Inscription: H&A”. This note on the GIA certificate simply indicates that “H&A” was laser inscribed on the diamond before it was graded by GIA. Neither the “H&A” laser inscription, nor the corresponding note on the GIA certificate, is an indication that the GIA observed hearts and arrows patterns on the diamond.
The diamond industry is still somewhat behind the latest technological advances in hearts and arrows precise optical symmetry, and thus have not established firm criteria for evaluating stones on this level. For consumers looking to purchase stones of this cut quality it is best to review hearts and arrows images under a H&A viewer.

